SHARE
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disorder that primarily affects the joints, causing pain, swelling, and stiffness. Did you know RA can also affect multiple other organs, including your lungs? Yes, unfortunately, chronic inflammation in RA can affect the lungs in multiple ways.
This article delves into the multifaceted aspects of this connection, exploring the impact on respiratory health, diagnostic challenges, treatment approaches, and the human side of living with both conditions.
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis
RA is an autoimmune condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues, leading to joint and multiple organ inflammation. Although a specific cause is unknown, the genetic and environmental factors contribute to its onset the most.
Symptoms of RA
Identifying RA early is crucial. Symptoms include joint pain, morning stiffness, fatigue, and swollen joints, often symmetrically affecting both sides of the body, most often both hands and feet but also other joints such as knees, ankles or shoulders.
Link Between Rheumatoid Arthritis and Lung Complications
Recent research has shed light on the link between RA and lung complications. Studies indicate a higher prevalence of respiratory issues among RA patients with aggressive forms or untreated. There are patients that will develop lung complications if they were not diagnosed early.
Types of Lung Complications

From interstitial lung disease to pleuritis (inflammation of the lungs lining) to lung nodules, the spectrum of lung complications associated with RA is diverse. Understanding these is vital for comprehensive care.
Interstitial lung disease is the most common form of RA complication and involves the thickening or stiffness of the lung tissue. As a result of this process, the patients will start developing shortness of breath, first with exercise, then gradually to rest. Many patients will require oxygen supplementation to help their breathing.
Pleuritis (inflammation of the lining of the lungs) or fluid in the lungs is also a possible complication of RA. Most patients will develop chest pain, back pain or pain when they take a deep breath.
Upper Airway Obstruction refers to difficulties involving the upper part of the respiratory tract. Some patients , due to inflammation of the cricoarytenoid joint (the area around the vocal cords) will cause changes in the voice, difficulties to swallow, pain with coughing or swallowing. The changes in this cricoarytenoid joint are visible using laryngoscopy by an ENT physician.
It can also be present in the lungs. They can be single or multiple. The nodules can cause complications like pneumothorax (lung rupture and colapse) and can also mimic a cancer/ tumor. The only way to differentiate between lung cancer and a rheumatoid arthritis nodule is to obtain a tissue biopsy which is essential especially in smokers.
Some medications that we use for patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis, like Methotrexate (most frequently reported), Leflunomide and even TNF-alpha inhibitors (more rare) were reported to cause lung toxicity cause
hoarseness, involvement. Thus, a chest X-ray is recommended before starting treatment for RA.
How RA Affects the Lungs
RA’s inflammatory processes can extend to the lungs, causing inflammation and scarring. This impacts lung function, leading to breathing difficulties.
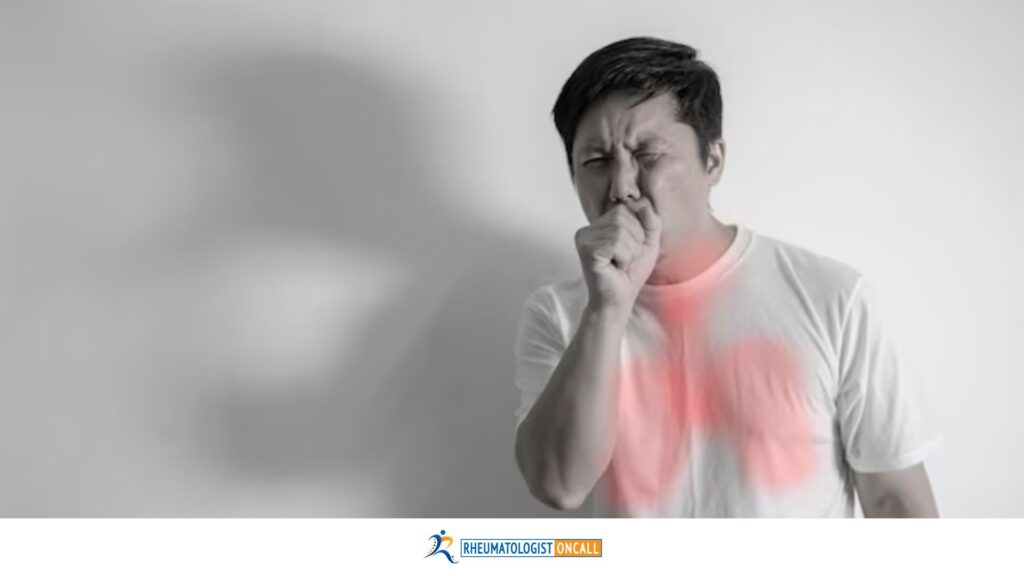
Breathing Difficulties and Related Issues
Patients often experience shortness of breath, persistent cough, and decreased lung capacity. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for timely intervention.
Diagnostic Challenges
The challenge lies in distinguishing RA-related lung issues from other respiratory conditions. Specialized tests and close monitoring become essential. Chest X Rays, CT scans and Pulmonary function tests are essential to evaluate patients with lung complications. At times, obtaining fluid from the lungs or a tissue biopsy can add a lot of value to determining the diagnosis.
Treatment Approaches
A comprehensive approach involves medications targeting RA and lung involvement. Coordination between rheumatologists and pulmonologists is key. There are multiple aspects that need to be considered and many times the treatment has to address both the Rheumatoid arthritis and the lung disease.
Lifestyle Changes and Therapies
Beyond medications, lifestyle modifications such as smoking cessation and regular exercise play a pivotal role. Pulmonary rehabilitation may be recommended for respiratory support and will improve the lung capacity, making patients breathe better.
Coping Mechanisms
Living with RA and concurrent lung issues can be challenging. Emotional support, self-care practices, and coping strategies empower individuals to navigate these challenges.
Connecting with support groups and communities provides a sense of understanding and shared experiences. Peer support can be invaluable in the journey of managing both conditions.
Mind-Body Connections and Their Impact
Mindfulness, meditation, and stress reduction techniques contribute to a holistic approach, fostering overall well-being for individuals managing RA and respiratory challenges.
Hope for Improved Outcomes
As research progresses and medical advancements unfold, there is hope for improved outcomes, enhancing the quality of life for those facing the dual challenge of RA and lung complications. Recognizing the signs, understanding the impact on respiratory health, and adopting a proactive approach to management are essential components of navigating this dual challenge.
As we’ve explored the various facets of this connection, it becomes evident that early intervention and holistic care are pivotal. Beyond medical treatments, lifestyle adjustments, emotional support, and staying informed about advancements contribute significantly to enhancing the overall well-being of individuals facing both RA and lung complications.
If you find yourself in need of expert guidance, consider exploring the services of Rheumatologist Oncall, our dedicated telemedicine company specializing in rheumatological care. Our experienced rheumatologists are just a call away, ready to provide personalized assistance and support tailored to your unique needs.
Don’t let Rheumatoid Arthritis and its potential lung complications hinder your quality of life. Take charge of your health, stay connected with professionals, and embrace the possibilities of improved well-being. Remember, your journey is important, and proactive steps today can lead to a more comfortable and fulfilling tomorrow.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Can Rheumatoid Arthritis directly cause lung complications?
While RA primarily affects joints, the inflammatory processes associated with the condition can extend to the lungs, leading to complications.
What are the common symptoms of RA-related lung issues?
Breathing difficulties, persistent cough, chest pain, changes in voice and decreased lung capacity are common symptoms that individuals may experience.
How can one reduce the risk of lung complications with RA?
Strategies include early diagnosis, effective RA management, smoking cessation, vaccination, and environmental precautions.
Is there a cure for RA-related lung complications?
While there isn’t a cure, advancements in treatments offer hope for improved outcomes. Management involves a combination of medications and lifestyle adjustments.
Where can individuals find support for dealing with both RA and lung complications?
Support groups, online communities, and healthcare professionals can provide valuable support and insights for individuals navigating these challenges. Our company is here to support you, contact us at Rheumatologist OnCall.