SHARE
How many times have you heard that stress is detrimental to your health? Research shows that high stress levels can actually trigger the onset of autoimmune diseases, like Rheumatoid Arthritis. Being diagnosed with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) not only will cause pain, but will trigger additional stress that will worsen the symptoms. This is a vicious cycle. Thus, managing stress should be a priority for Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) patients.
This article will explore the scientific links between stress and Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) and will discuss how to manage stress as a part of your arthritis treatment plan.
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis
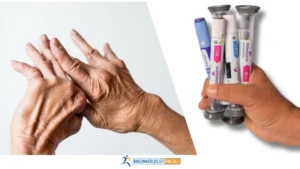
First, a quick recap of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA). It is an autoimmune disorder affecting over 1.4 million adults in the US, causing chronic inflammation within the joints, resulting in progressive cartilage and bone damage.
Key characteristics of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA):
- Most commonly affects the smaller joints – hands, wrists, feet
- An autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks joint tissue
- Joint pain, swelling, stiffness and eventual loss of function
- Can lead to deformities and disability without treatment
- More common in women than men
- Often begins between ages 30-60
While there is no cure, the right medications and lifestyle habits can effectively control Rheumatoid Arthritis inflammation and symptoms. Let’s discuss how stress ties into rheumatoid arthritis.
The Physiology of Stress

When we experience mental, emotional or physiological stress, it activates the sympathetic nervous system, also known as the “fight or flight” response. This triggers the release of stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline.
In small doses, these stress hormones are protective and increase immune function. However, chronic stress leads to constant elevated levels of cortisol throughout the body. This disrupts nearly every body system.
Prolonged high cortisol also suppresses the immune system over time, increasing susceptibility to infections and disease.
How Stress Impacts Onset of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Research indicates that chronic stress may be one environmental factor that triggers rheumatoid arthritis in genetically predisposed individuals.
Studies show that prolonged stress alters inflammatory pathways in the body relevant to Rheumatoid Arthritis development. Stress exposure also changes gene expression of certain HLA genes associated with higher Rheumatoid Arthritis risk.
Additionally, emotional stress may cause epigenetic changes that influence immune function and inflammation. High stress essentially generates the perfect environment within the body for autoimmunity and rheumatoid arthritis to develop.
Managing stress and promoting relaxation is especially important for those with a family history of rheumatoid arthritis and other risk factors. Decreasing stress where possible may help delay or prevent Rheumatoid Arthritis onset.
How Stress Exacerbates Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms
Once rheumatoid arthritis is established, uncontrolled stress also worsens key Rheumatoid Arthritis symptoms:
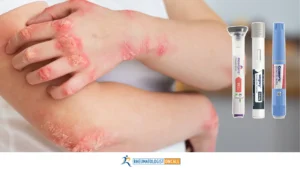
- More inflammation – Stress hormone release directly increases inflammatory cytokines like IL-6 and TNF-alpha central to Rheumatoid Arthritis joint damage progression.
- Increased pain – Stress lowers pain thresholds and amplifies pain perception through multiple pathways.
- Greater fatigue – Chronic stress leaves Rheumatoid Arthritis patients utterly exhausted mentally, physically and emotionally.
- Higher disease activity scores – Unmanaged stress correlates to measurable jumps in Rheumatoid Arthritis disease activity and joint deterioration.
- More frequent flares – Stress overload is commonly cited as a flare trigger among rheumatoid arthritis patients.
- Decreased sleep quality – Anxiety and worrying at night interrupts already poor sleep in many Rheumatoid Arthritis patients.
Clearly, abnormally high stress levels translate directly to heightened rheumatoid arthritis symptoms and progression. Learning positive coping mechanisms to manage stress is vital.
Stress Management Tips for Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients
Here are some research-backed tips for reducing stress:
- Practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, yoga, or tai chi. Even 5 minutes helps.
- Maintain social connections since isolation increases stress hormone levels.
- Focus on positive emotions and gratitude to counteract negativity and rumination.
- Set reasonable limits and pace yourself instead of over-scheduling.
- Exercise moderately most days of the week to naturally lower stress hormones.
- Try journaling, art therapy or music therapy for creative stress relief.
- Avoid unhealthy coping mechanisms like smoking, excessive drinking or emotional eating.
- Get adequate sleep since exhaustion itself is a major stressor.
Work collaboratively with your rheumatologist to find personalized stress management strategies.
Take Control of Your Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms
Managing rheumatoid arthritis requires a multi-pronged approach. Don’t underestimate the enormous role stress plays in Rheumatoid Arthritis onset and symptom severity. Making stress relief a priority through healthy coping techniques can make a real difference.
Commit to working on positive stress management. Staying physically and mentally relaxed helps keep Rheumatoid Arthritis disease activity and inflammation in check. There are many ways to take control of stress – start implementing them today to take control of your rheumatoid arthritis symptoms.
At Rheumatologist OnCall, our patient-first approach to Rheumatoid Arthritis care focuses on the whole person, not just the disease. We recognize that effectively treating and managing this challenging autoimmune condition requires more than medication alone. Our comprehensive Rheumatoid Arthritis treatment model addresses the interconnected relationship between mind, body and lifestyle factors. Our goal is to help patients achieve disease remission and an improved quality of life. We provide the tools not just to cope with Rheumatoid Arthritis, but to actively thrive in the face of this diagnosis. Education on managing inflammation through nutrition empowers patients to make sustainable diet changes. Physical therapy maintains joint health and function. Mindfulness training helps build resilience against pain and fatigue.